eCommerce and the impact of Data Privacy Day

According to The Economist, the world’s most valuable resource is data, to the point of being considered the “oil of the digital age.” With the rise of personalisation and the implementation of artificial intelligence, a new concern arises on the horizon: data privacy. A truly personalised relationship between brands and customers is possible by accessing users’ personal information to analyse the data and predict behaviours. However, the negligent use of the data can have serious consequences.
This is one of the main reasons that motivated the creation of the International Data Privacy Day, which is celebrated every January 28th. The idea is to raise awareness about the importance of data privacy and to promote best practices. Currently, this day takes place in the United States, Canada, and 47 European countries including the United Kingdom and Spain.
The Data Privacy Day educational initiative originally focused on raising awareness. Another goal is to understand the importance of protecting personal information online, particularly in the context of social media. It also takes into account the effect that security breaches can have on governments, businesses and the general audience.
Personalization versus Data Privacy
Since the arrival of the GDPR, many companies were forced to adjust their practices related to the acquisition of users and new subscribers, as well as the type of data requested. The reason had to do with access to this information by third parties without consent. The abusive behaviour of those partners when managing the data was also in place. We are talking from receiving multiple promotional emails to sharing information online.
Privacy is an important and very serious issue. But, it is also a double-edged sword for the full implementation of personalisation. On the one hand, the more data a user provides, the better the AI will work. Thus, the customisation will reach maximum efficiency. But having a reckless attitude towards your users’ data can deeply affect your brand reputation and credibility.
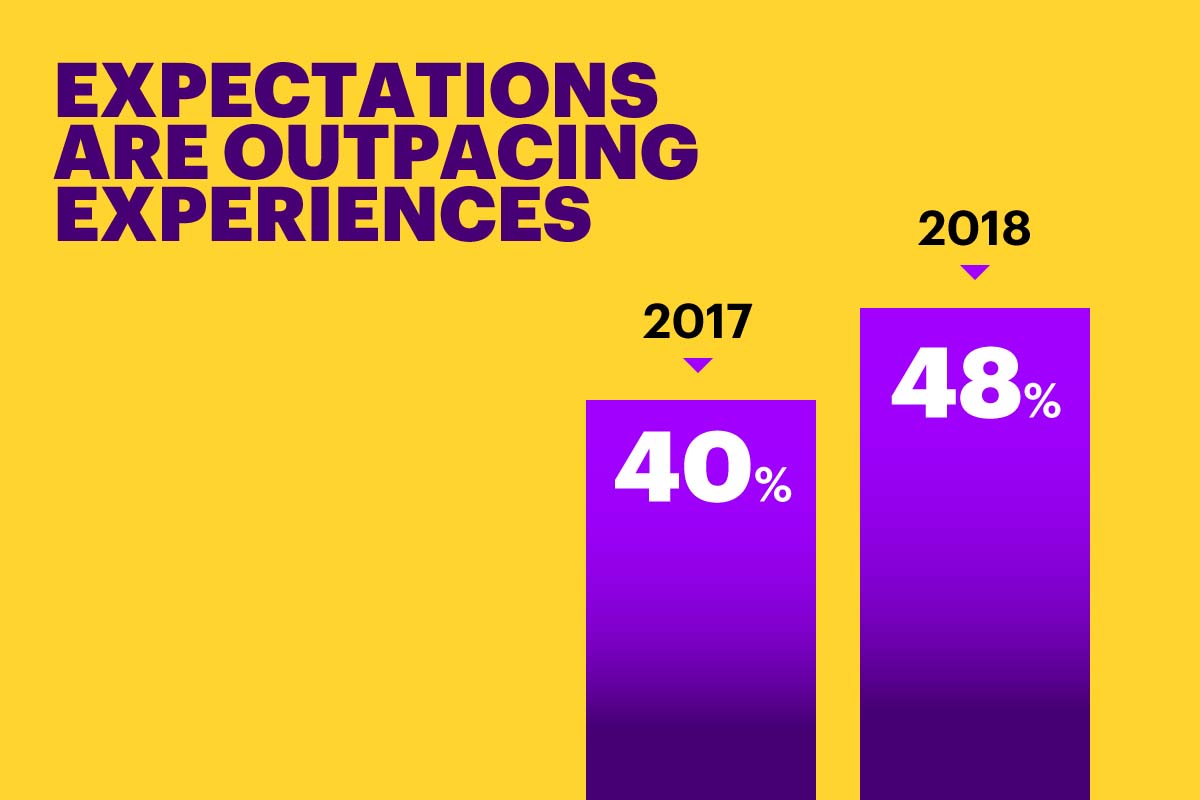
A report published by Accenture found that 83% of customers are willing to share their data with companies, if they obtain a clear benefit and if the relationship is respectful and transparent. In fact, in 2018, 48% of all consumers have left a business’ website and made a purchase elsewhere because the experience was poorly curated.
However, security breaches and the growing concern on online security has made this relationship going through a hard time. And, it is making personalisation more difficult for e-commerce companies.
Tips to preserve the privacy of your users:
- Always, regardless of the circumstances, ask your users for consent. From transactional emails to marketing communications. Even if this entails losing some potential customers. If someone is visiting your website, it means that the person likes your brand and it is willing to receive these communications.
- When it comes to the checkout process, always use payment platforms that encrypt user data, such as PayPal. Large payment gateways respect privacy policies throughout the world and allow you to have a cross-border practice.
- Communicate the use of cookies and request the consent clearly and visibly. The behavioural data – which allow personalising your relationship with your clients – come from the browsing and actions that a person performs while visiting your website, and although it is not a tangible process for the visitor, it must be aware.
How to protect privacy without affecting Artificial Intelligence?
Personalisation, as well as artificial intelligence, are here to stay. AI tools help provide predictive information about customers’ behaviour by using advanced algorithms. This allows not only to analyse historical data but also to provide operational support to companies. Not only does AI work for personalisation, but data security based on artificial intelligence can help quickly identify any anomaly. For example, in the case of email marketing, these solutions analyse each email message completely. This includes metadata, content, links and attachments.
In general, many companies use AI at two levels: to analyse behavioural data, predict patterns and adjust their business strategy. On a second level, as a security agent. By monitoring data flows, this technology can identify strange behaviours and thus prevent attacks or security breaches.
The use of AI to protect the privacy of data can greatly help companies identify all confidential information and track and control all movement inside and outside the company. AI-driven technology can help not only in personalising and improving the relationship between your brand and users but also ensuring that the organization always meets and controls all standards and privacy guidelines.